Status Report
Summary
We thought it is hard for us to achive something in two weeks by doing the battle agent. Therefore, we changed out goal into solving the maze problem by using deep q-learning algorithm. And the goal is that agent can find a way to the destination in the maze (shorter ways are preferred).
The input is the map, the agent’s current position, time elapsed. The agent should be able to decide where to move according to the map and its current position. The output will be the continuous moves taken by agents till the end of the game (either the agent reaches the goal or fall).
Approach
Our maze is a 10x10 matrix, with 20% of maze are gap (wall). The maze is made of dimand_block as floor, grass as wall, start at an emerald_block, and the destination is a redstone_block. We view the maze from a 21x21 grid, and store the position information. We store the whole grid as our states by replacing one index as “self” after moving. We have four different actions - move north, move south, move west, and move east. We calculate the reward as - 100 for reach the goal, -1 for each movement, -50 for touching the wall. Since we use the grid to store information, we add codes that will stop the agent move beyond the maze.
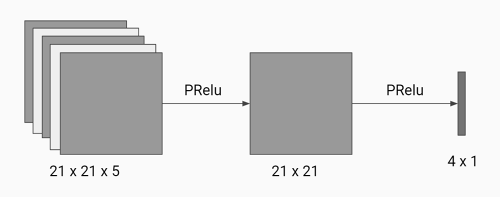
We use the Deep Q-learning algorithm to train the agent. We represent each state by the 21x21 map specifying the positions of the agent, the goal, lands, and dangerous stones, denoted by number 0-4. We use a neural network with three Dense layers both having PRelu as activate function. The neural network takes a 21x21xbatch_size matrix as input, and ouputs a 1x4 action matrix that each index indicates the rewards by choosing four different actions. The neural network has one hidden layer with the same size as input layer. And update the old reward by using the function:
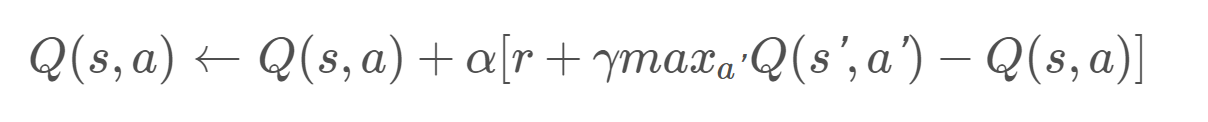
And we use MSE as out loss function.
After several tries, we found that the learning is not as good as expected. We adopted the suggestion from TA Mr. Stephen McAleer that we start at random position to let the agent learn each part of maze seperately so that it will not get stuck at the beginning of the maze. We use teleport command before each run to let agent go to a random position. We subdivide the maze into differnet areas, and teleport the agent to areas that are close to the destination first, then move towards to the beginning.
Evaluation
Quantative Metrics: Steps taken – By taking each move the agent will receive a small negative reward (-1)
Death – On moving to a stone, the agent will die and receive a large negative reward (-50)
Reaching a new position – By exploring a position that the agent has never been to, the agent will receive a small positive reward (+2)
Reaching the goal – When the agent reaches the goal, the game will end and the agent will receive a large positive reward (+100).
The rewards mentioned above are used for both training and evaluation. Also the evaluation of the agent’s performance will be based on the ratio of the number of solved mazes over the total number of mazes.
Qualitative Metrics: It will be impressive if this algorithm can reach the goal by following the shortest path with a high success rate. Otherwise it is also good to reach the goal successfully without touching stones.
Remaining Goals and Challenges
Still the maze cannot be perfectly solved. And we will continue improving algorithm by:
1. Building a different model that take the position as input of neural network rather than the whole grid, and for each action, we get the seperate output to evaluate which is the best one.
2. Probably change the reward function, that is now for each time it reaches the goal, the loss function will increase dramatically. And after the discount factor close to 0, the “best” action our agent will choose is moving towards the wall rather than to the goal. This may be because our reward function is not fitted to our method.
3. Probably in the future, we could add monsters in the maze, and the agent will learn how to kill those monsters to keep himself safe until reaching the goal.<\p>